Is The Name Of A Bacteria Found In Soil And Water And Some Animals, Including Poultry And Cattle.
Links toPEDv (Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus).
Microorganisms
Microorganisms (e.thousand. virus, bacteria, protozoa, and fungi) environs us, on u.s.a., and in the states; they are ubiquitous and everything in the earth is governed past them. They are role of our everyday lives. They influence the the quality of our soil, food grown on that soil, and how our body reacts to that food. They are various, ranging from a simple mix of protein and Deoxyribonucleic acid to complex multi-cellular small "animals". Most environmental microorganisms spend their unabridged lives every bit quiet members of their ecological gild, simply some accomplish a level of infamy. Pathogens may simply stand for a very small portion of all microorganisms, but they are ofttimes the almost visible, thanks to readily reported outbreaks, food recalls, and proliferation of internet news blogs and sites.
What is a Pathogen?
A pathogen is a biological amanuensis that causes disease or affliction; this affliction can occur in humans, animals, or crops. Zoonotic pathogens refers to pathogens naturally transmitted from animals to humans and are often heard about on news sites or involved in nutrient recalls.
All animals including pets, livestock, wild fauna and humans, are possible hosts of potential human pathogens. Nosotros will focus on pathogens originating from livestock and poultry that might exist transported to humans via air, water, soil, crop, and fomites (inanimate objects) contacted direct or indirectly by manure.
Zoonotic Pathogens
In that location are iv general classes of zoonotic pathogens:
- viruses
- bacteria
- protozoan parasites
- helminth parasites
Zoonotic viruses are those found mainly in animals that cause illness in people who come into contact with the animal or share a vector (transmitter of disease) similar a mosquito (West Nile Virus is a virus of birds which mosquitoes carry and tin transmit to people). Viruses can but multiply when they are inside a host cell.
- Until very recently, it was considered that nearly fecal or urine transmitted viruses of livestock were not zoonotic, but things have changed somewhat in recent years, and nosotros are now in a steep learning bend every bit to how important ruminants and poultry are every bit reservoirs of these zoonotic viral agents.
Zoonotic bacterial pathogens are, like all bacteria, unmarried celled microorganisms that can survive and, under favorable weather condition, reproduce in terrestrial and aquatic environments. The zoonotic leaner are those that typically wheel in domestic animals without causing affliction in their typical hosts. However, when they become transmitted into people, the affliction that is produced can be severe.
- Examples of zoonotic bacteria are Salmonella spp., strains of Escherichia coli such as Eastward. coli 0157:H7, Listeria monocytogenes, and Campylobacter spp.
Zoonotic protozoan parasites, are protozoa that are constitute in other animals and which can infect people. There are basically ii roles that humans can play in this scenario. They can be accidental hosts in the life cycle of the protozoan, where the protozoan undergoes the aforementioned evolution in the human being as it does in its normal reservoir host. Or, the human may be an intermediate host in the life bike of the parasites, merely similar whatever other vertebrate; in this example, the reservoir host shed many stages into the environment with the goal of infecting as many intermediate hosts equally possible.
- In the case of zoonotic protozoa relative to domestic farm animals, only a few have proven to be of pregnant concern relative to the infection of people.
- Species of Cryptosporidium constitute in horses, cattle, pigs, and sheep can accidentally infect people, with C. parvum of young ruminants beingness the well-nigh common offender.
- Giardia of livestock typically does non seem to occur in people, just it does seem that they might be infected with the human form and could then serve equally a source of stages that might be passed to humans.
Zoonotic helminth parasites are worms, nematodes (roundworms), cestodes (tapeworms), or trematodes (flukes), that have cycles similar to protozoa. Again, people tin exist infected accidentally past the worm in the same manner as a reservoir host or they can exist serving equally only another vertebrate intermediate host in the life bike of the parasite.
- Fortunately, in the case of domestic farm animals, the helminth parasites are for the virtually function not zoonotic with respect to people. The but forms with stages that might be infectious to people from manure would exist the egg of the pig roundworm, Ascaris suum.
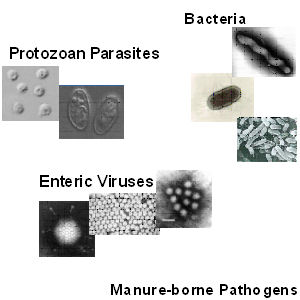
Photograph source: Jeanette Thurston-Enriquez webcast presentation.
Detailed word of protozoan parasites, leaner, and viruses tin be found on pages 5, 12, and 18, respectively, of the USDA NRCS technical notation
Waterborne Pathogens in Agricultural Watersheds
Several outbreaks of human illness and death have been attributed to drinking water contaminated with livestock manure. Of 66 drinking water outbreaks in affluent nations, the probable crusade of 12 of the outbreaks was livestock manure (run into Hrudey and Hrudey, 2004 in Research Summaries. These included:
- An outbreak at the 1999 Washington County Off-white, New York (East. coli O157:H7; of 781 confirmed cases, 71 people were hospitalized, and two died);
- An outbreak in Walkerton, Ontario, Canada in 2000 (E. coli O157:H7 and Campylobacter jejuni; 2,300 people were ill, 65 were hospitalized and 7 died).
These outbreaks were indicative of the capability of the pathogens to survive and exist leached through soil to groundwater sources of drinking h2o.
Not all affliction outbreaks are livestock related. For instance, animal manure was initially suggested as the source of the largest drinking water outbreak in U.S. history – the Cryptosporidium outbreak in Milwaukee, WI in 1993. Several years later post-obit advances in microbiology and genetics, human being sewage was identified every bit the likely contributor.
Antibody Resistant Bacteria in Agricultural Manures
An antibiotic-resistant bacterial population is ane in which resistance is either intrinsic or has been acquired from exposure either to antibiotics or to other antibiotic resistant bacterial populations. The increased frequency of antibody resistant pathogens has become a serious public health concern as demonstrated with outbreaks of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and antibiotic resistant Salmonella such equally Salmonella DT104. Little research and information is bachelor on the presence of antibody resistant bacteria originating in manure and manure land applied environments, and, thus, little is known about their fate and transport in soil, water, crops, and agronomic systems.
A listing of possible zoonotic pathogens can exist found on pages 6 – 10 of an EPA literature review.
Authored by: Michael Jenkins and John Brooks, USDA ARS, Dwight Bowman and Janice Liotta, Cornell University.
Question or concerns, contact John Brooks (john.brooks@ars.usda.gov)
Source: https://lpelc.org/pathogens-and-potential-risks-related-to-livestock-or-poultry-manure/
Posted by: robersonbles1976.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is The Name Of A Bacteria Found In Soil And Water And Some Animals, Including Poultry And Cattle."
Post a Comment